Appearance
七、vm.$watch
功能
监听$data中成员的变化,观察 Vue 实例变化的一个表达式或计算属性函数。回调函数得到的参数为新值和旧值。表达式只 接受监督的键路径。对于更复杂的表达式,用一个函数取代。
参数
- expOrFn:要监视的 $data 中的属性,可以是表达式或函数
- callback:数据变化后执行的函数,接收两个参数,新值和旧值
- 函数:回调函数
- 对象:具有 handler 属性(字符串或者函数),如果该属性为字符串则 methods 中相应 的定义
- options:可选的选项,重点介绍
- deep:布尔类型,深度监听
- immediate:布尔类型,是否立即执行一次回调函数
示例
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Vue.js 01 component example</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{ user.fullName }}
</div>
<script src="../../dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
user: {
firstName: '张',
lastName: '三',
fullName: ''
}
}
})
vm.$watch('user',
function (newValue, oldValue) {
this.user.fullName = newValue.firstName + newValue.lastName
}
)
</script>
</body>
</html>这样一开始的时候不会立马执行,想要立马执行就在第三个参数中添加选项
js
vm.$watch('user',
function (newValue, oldValue) {
this.user.fullName = newValue.firstName + newValue.lastName
},{
immediate: true
}
)此时就会立即执行,页面展示张三
下面改变user的值
- 将user置为{}
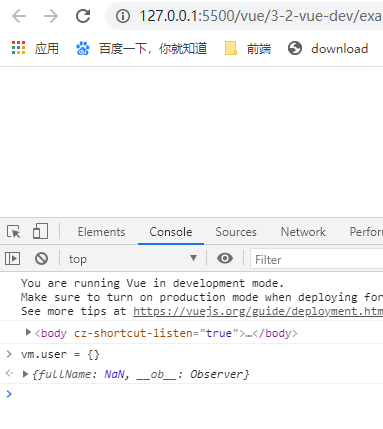
修改user的值可以看到页面进行了响应式变化
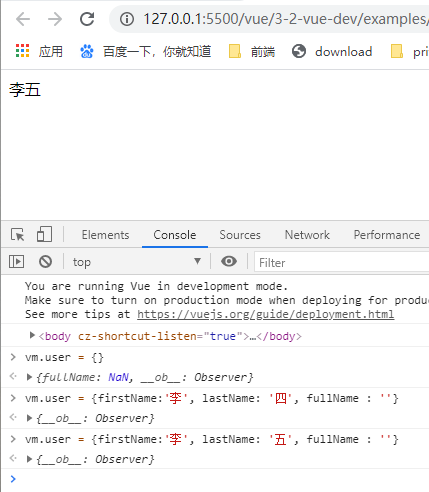
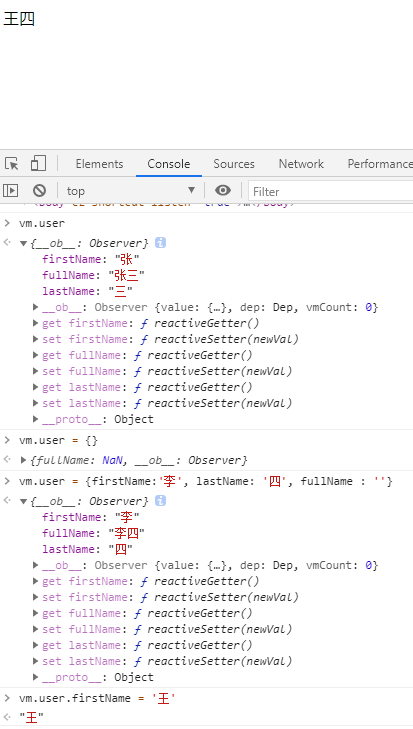
- 将user的firstName改为李
这个时候并没有进行改变,要想监听,可以这样写
js
vm.$watch('user.firstName',
function (newValue, oldValue) {
this.user.fullName = newValue + this.user.lastName
},{
immediate: true
}
)
vm.$watch('user.lastName',
function (newValue, oldValue) {
this.user.fullName = this.user.firstName + newValue
},{
immediate: true
}
)
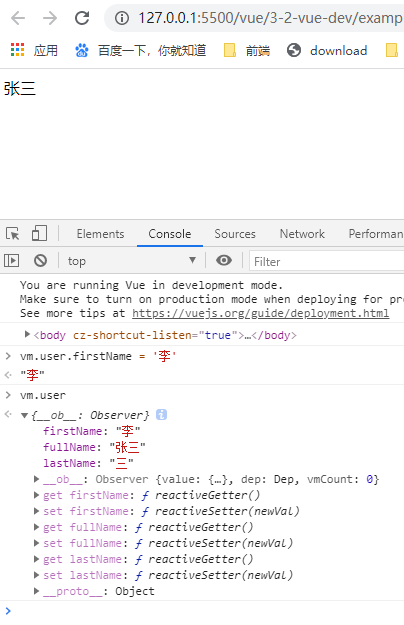
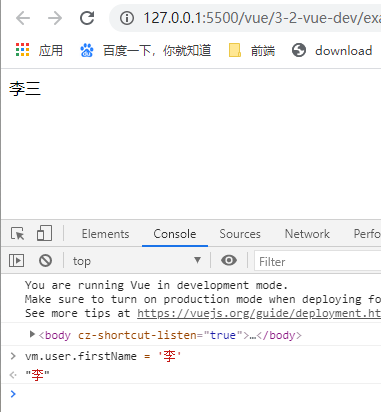
这样就比较麻烦,每个相关的属性都要写,推荐这样写,在第三个参数配置中写deep深度监听
js
vm.$watch('user',
function (newValue, oldValue) {
this.user.fullName = newValue.firstName + newValue.lastName
},{
immediate: true,
deep: true
}
)
watcher的讲解
三种类型的 Watcher 对象
- 没有静态方法,因为 $watch 方法中要使用 Vue 的实例
- Watcher 分三种:计算属性 Watcher、用户 Watcher (侦听器)、渲染 Watcher
- 创建顺序:计算属性 Watcher、用户 Watcher (侦听器)、渲染 Watcher
调试watcher渲染顺序
源码解析
我们对$watch的源码进行解析
从initState里面看到调用了initWatch方法,initWatch方法对用户传入的属性进行遍历,
js
function initWatch (vm: Component, watch: Object) {
// 遍历用户传入的watch的属性,这里是user
for (const key in watch) {
// 获取watch的值,可以是数组,也可以是对象,函数
const handler = watch[key]
// 如果是数组,就对元素进行遍历,每一个元素都创建watcher,当这个属性变化的时候,会执行多个回调
if (Array.isArray(handler)) {
for (let i = 0; i < handler.length; i++) {
createWatcher(vm, key, handler[i])
}
// 如果不是数组,直接执行createWatcher
} else {
createWatcher(vm, key, handler)
}
}
}那么createWatcher中是怎么定义的呢?
js
function createWatcher (
// Vue实例,对应属性,和handler
vm: Component,
expOrFn: string | Function,
handler: any,
options?: Object
) {
// 先判断handler是否是一个原生对象
if (isPlainObject(handler)) {
options = handler
// 真正的handler,回调函数
handler = handler.handler
}
// 判断handler是否是字符串,如果是字符串就会去实例对象上找,也就是methods中定义的方法
if (typeof handler === 'string') {
handler = vm[handler]
}
// 将解析好的数据给$watch
return vm.$watch(expOrFn, handler, options)
}下面我们进入$watch函数,也在当前文件中,搜索跳转
js
//原型上挂载了$watch,监视数据的变化
Vue.prototype.$watch = function (
expOrFn: string | Function,
cb: any,
options?: Object
): Function {
// 获取当前实例,没有对应的静态方法,因为其用到了vue的实例
const vm: Component = this
// 判断回调函数是否是原生对象,如果是继续放到createWatcher中,这里要保证回调函数是函数
if (isPlainObject(cb)) {
return createWatcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options)
}
// 把当前watch的属性赋值,如果没有赋值空对象
options = options || {}
// 标记为用户watcher
options.user = true
// 创建用户watcher对象
const watcher = new Watcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options)
// 判断选项中是否要立即执行
if (options.immediate) {
try {
// 如果是就立刻调用回调函数,使用call改变其内部指向为vue实例,并将值返回
// 使用try-catch是不确定我们传入的代码是否安全,不要阻塞之后的代码执行,
cb.call(vm, watcher.value)
} catch (error) {
handleError(error, vm, `callback for immediate watcher "${watcher.expression}"`)
}
}
// 返回取消监听的方法
return function unwatchFn () {
watcher.teardown()
}
}那user只是定义了没有看到有使用的地方,现在调转到Watcher中看做了什么,在watcher.js中搜索user
- 将this.user设置为true
- get方法中
js
get () {
// 调用pushTarget,将当前的Watcher对象放入栈中
// 每个组件对应一个Watcher,Watcher会去渲染视图,如果组件有嵌套的话会先渲染内部的组件,所以要将父组件的Watcher先保存起来,这是这个pushTarget的作用
pushTarget(this)
let value
const vm = this.vm
try {
// 最关键的一句话
// 这句话调用了getter,getter存储的是传入的第二个参数,且是函数,首次渲染是updateComponent,所以在get方法的内部调用了updateComponent,并且改变了函数内部的this指向到Vue实例vm,并且传入了vm
// 这里将虚拟DOM转化成了真实DOM并更新到页面中
// 如果是用户watcher的话,这个getter是获取属性的,如果在获取属性的时候有异常,下面会处理异常,这里不看
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)
} catch (e) {
if (this.user) {
handleError(e, vm, `getter for watcher "${this.expression}"`)
} else {
throw e
}
// 执行完毕之后会进行清理工作
} finally {
// "touch" every property so they are all tracked as
// dependencies for deep watching
if (this.deep) {
traverse(value)
}
// 将watcher从栈中弹出
popTarget()
// 会把当前watcher会从dep.subs数组中移除,把watcher里面的dep也移除
this.cleanupDeps()
}
return value
}- run方法
js
run () {
// 标记当前watcher是否是存活的状态,默认为true,可处理
if (this.active) {
// 调用其get方法,如果是渲染watcher会调用getter,执行updateComponent方法渲染DOM更新页面
// 之后用value记录返回结果,如果是渲染watcher没有返回结果,value是undefined,渲染函数的cb是noop空函数.
// 如果是用户watcher,继续执行,获取旧值记录新值,调用cb回调函数,侦听器的function就是回调函数,
const value = this.get()
if (
value !== this.value ||
// Deep watchers and watchers on Object/Arrays should fire even
// when the value is the same, because the value may
// have mutated.
isObject(value) ||
this.deep
) {
// set new value
const oldValue = this.value
this.value = value
if (this.user) {
// 如果是用户watcher,添加异常处理
try {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, this.vm, `callback for watcher "${this.expression}"`)
}
} else {
// 如果是其他watcher,直接调用
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue)
}
}
}
}通过源码可以看出来,watcher中的属性可以传数组,也可以是对象,也可以是函数,里面的handler也可以嵌套
js
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message:'Hello Vue',
user: {
firstName: '张',
lastName: '三',
fullName: ''
},
count: 0
},
computed: {
reversedMessage: function () {
return this.message.split('').reverse().join('')
}
},
watch: {
// 这里不给user.firstName和lastName单独设置watcher,是因为没有办法配置立即执行immediate和深度监听deep
// 监听对象user,要提供handler,就是回调函数,还有配置立即执行immediate和深度监听deep
// 在侦听器里面,当数据变化的时候,还可以做异步处理这些更复杂的内容
'user': [{
handler: function (newValue, oldValue) {
this.user.fullName = this.user.firstName + this.user.lastName
},
deep: true,
immediate: true
}, {
handler: function (newValue, oldValue) {
this.count++
},
deep: true,
immediate: true
}]
}
})